Welcome to Bounty Boulevard State
School. We look forward to working with you on your child’s learning journey.
This information is updated each year to reflect current policy
and practice.
Schools & teachers plan for
every student to participate and learn. Students with disability join in the
same curriculum activities & learning programs as other students in the
class with the support of suitable adjustments. This involves explicit teaching
and scaffolded learning, teaching both the concepts on which the task is based
and the language demands of the task, enabling all students to participate in
the curriculum. Schools support students by using differentiated teaching
practices, assistive technology and where necessary focused and intensive
teaching. (DET One Portal)
Students with a disability are supported
through school processes detailed in this document. Disabilities can include
such diagnoses as Dyslexia, Dyspraxia, Anxiety and general learning
disabilities in addition to those categories supported through Special
Education Program (SEP).
Structure
Inclusive Educational Benefits:

Parents want their children to be accepted by their peers, have friends and lead "regular" lives. Inclusive settings can make this vision a reality for many children with disability.
Respect and understanding grow when children of differing abilities, cultures and backgrounds play and learn together.
Schools are important places for children to develop friendships and learn social skills. Children with and without disability learn with and from each other in inclusive classes.
In inclusive classrooms, children with and without disability are expected to learn. With high expectations and good instruction children with disability learn academic skills. Because the philosophy of inclusive education is aimed at helping all children learn, everyone in the class benefits. Children's individual needs are met and they learn within a nurturing environment
Positive self–identity, especially as students get older, may be
developed through positive relationships with peers. As with students without
disability, students with disability require positive relationships with peers
to help them learn about themselves.
In supporting a student with disability it is critical staff:
Recognise the friendship needs of students
Recognise the student, like their peers, has the capacity to be a great friend.
Whole School Support
Possible members of the whole school team supporting the student in consultation with their parents/caregivers.
A whole school approach refers to a shared commitment to
quality teaching and improved student achievement that recognises diversity
(including students with disability) at school and classroom level.
This approach is
implemented by the whole school support team, consisting of a wide range of staff
supporting student access, participation and achievement.
A whole
school approach directs support to different levels of student need. Schools
identify the appropriate layer of support through analysis of student data and
ongoing monitoring of student progress. Support ranges through increasing
levels of adjustments, monitoring of student learning and behaviour, and
involvement of support staff and can include Differentiated Teaching, Focused
Teaching or Intensive Teaching.
STAFFING:
Special Education Programs (SEP) supports students under the
Education Adjustment Program (EAP) in the areas of: Autism Spectrum Disorder, Intellectual
Disability, Speech Language Impairment, Vision Impairment, Hearing Impairment,
Physical Impairment
Students who are diagnosed under one of the six EAP
categories must go through a complex process of Verification and Profiling in
order to meet criteria. Paperwork is submitted online and it takes some time
for this to be processed by the verification team. Each student who is verified, has an Educational
Adjustment Profile completed by the Support Teacher with the Class Teacher,
which notes type and frequency of adjustments needed. Resourcing is not student
specific.
Students with other disabilities, including Dyslexia,
Dyspraxia, ADHD, Anxiety, Diabetes and other conditions also have adjustments
made and recorded.
Student Support Team
School Support professionals including the Guidance Officer,
Head of Diverse Learners P to 2 and 3 to 6, Support Teachers, Therapists:
Speech Language, Occupational and Physiotherapists and Deputy Principals meet
with Class Teachers to hold case conferences to recommend strategies and
programs for Students referred by Class Teacher through parent consultation.
Class Teacher:
The Class Teacher is the primary
point of contact for all students and their parents. The Class Teacher teaches
the whole class, differentiates instruction for differing levels of needs in
the class and makes adjustments for students in the class.
Support Teacher:
Maintain documentation, (including AIMS and
Verification if supported under SEP/EAP); gather and analyse data; facilitate
and lead collaborative meetings with groups & for individual
students; manage resourcing; build capacity of staff, students and other
stakeholders; manage and support trained TAs; liaise with parents; provide
supportive programs and strategies for students to access lunch breaks,
excursions, specialist lessons and camps; access, plan and document
recommendations, equipment, strategies and programs for students in the areas
of Social Emotional Wellbeing, Health and Personal Care, Safety, Communication
& Curriculum
Support Teachers work in Curriculum and in Access-
Differentiation
layer: model inclusive,
needs based practices and adjustments in classes and groups, support class
teachers to build capacity.
Focused &
Intensive teaching layers:
build capacity with trained TAs, write focused teaching programs or access
quality evidence based programs, group students on a needs basis, monitor and
record progress of these students in Support Provisions. In collaboration with
Class Teachers, may also teach the class at times to allow class teacher to
work directly with students, work collaboratively with class teachers. Provide
direct support as accessible to identified students, accessing, resourcing,
implementing quality intervention programs.
Teacher Aide: Teacher Aides support Teachers to
implement in class and supplementary programs &:
Record
interventions and programs to provide feedback to Teachers; manage resources; liaise with Teachers;
inclusively provide support for students as directed to further those students’
access to lunch breaks, excursions, specialist lessons and camps; document
programs they have been entrusted with for students in the areas of Social
Emotional Wellbeing, Health and Personal Care, Safety and Communication,
Curriculum
Teacher
Aides work in Curriculum and in Access-
Differentiation
layer: Implement inclusive,
needs based practices and adjustments in classes and groups, support class
teachers to implement strategies and programs developed by teachers
Focused &
Intensive teaching layers: implementing focused /Intensive teaching programs
provided by Support Teacher or Class Teacher at group level, Provide direct support
to identified students, implementing quality intervention programs, record
progress of these students & report to Support Teacher or Class Teacher
Teacher Aide Support:
Promoting independence and
self–advocacy.
Learning
happens in many ways and places at school, not just in the classroom. For
example, we know students learn a lot about how to make and keep friends by
socialising with others before school, at break times and by learning as part
of a group. We also know students may develop resilience and confidence, and
learn how to solve problems by making mistakes and taking risks in a safe and
supportive environment such as a school.
When
students with disability are sheltered from making mistakes and taking risks
due to the intensity of adult support at school, they may learn to rely on this
support to help them learn. This may result in students not developing the
tools and strategies to learn and make decisions without intensive support.
Research
tells us that over–involvement by teacher aides or excessive close proximity to
teacher aides during support may have a negative impact on "student's
wellbeing, learning & social interaction with peers."
Some students with disability may be dependent on others to
help them with activities such as personal care, mobility or communication. It
is vital they do as much as possible for themselves, learn how to ask for help
and also how to refuse inappropriate assistance. Staff help students develop
skills they will require long term in managing their support–whether it is
offered by a family member, friend or an employed carer.
Support for students with disability needs to be provided in
such a way it promotes the student's inclusion, independence, choice &
connection with peers. Like all
students, those with disability benefit from learning:
it is OK to make mistakes
there are important lessons to be learnt from making mistakes
to take responsibility for the decisions and choices they have made and will need to make into the future
understanding what happens when they make certain decisions.
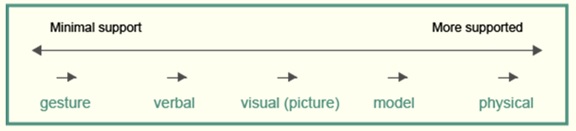
Cues and prompts are signals and messages that communicate
to a student they are required to behave or respond in a particular way or
complete a specific task. Cues and prompts can be visual, verbal or gestures
and are often paired together. For example, a gesture may be accompanied by a
verbal prompt. They are often designed to suit the specific needs of a student in
a particular context. For example they may be a hint, or they may show a
student how to complete a task step by step.
The correct use of cues, prompts and feedback
assists all students to learn. It is important to offer a level of support
which motivates students to be active learners. The amount and type of support
needs to be monitored so students do not become dependent on it. The goal is
for student to become as independent as possible. As a general rule, start with
the minimal support prompt.
Therapists
Students who are verified under the SEP/EAP have access to
therapists (DET Occupational Therapists, Physiotherapists and Speech
Therapists) to assist with programming recommendations. Requests for these
services are submitted and therapists take these through a process across their
allocated schools. Advice as to access can take some time after submission of
requests. Students with other disabilities benefit from the advice and
strategies provided by DET therapists. Reports by private therapists provided
by parents are welcomed to assist with adjustment planning.
GENERAL:
Behaviour:
All students are bound by the Bounty Boulevard State School
Responsible Behaviour Plan for Students.
Bounty Boulevard State School provides a network of student
support. Students are supported based on their individual needs and their
individual circumstances. Our program is framed through Positive
Behaviour for Learning (PBL) which ensures that students are taught expected
behaviours in a structured program which is reinforced through class processes.
When behaviour is inappropriate, the situation will be
assessed case by case to determine the support level that is required for the
student at that time. Support in the area of behaviour can include the
following: writing social stories to assist student to understand context, role
plays, support to attend Reflection room, debriefing to discuss concerns,
attendance at Supervised Play and Play plan showing location of play at
different breaks.
Some students may benefit from the provision and
implementation of an Individual Behaviour
Support Plan (IBSP) to ensure that all stakeholders have alignment in goals
and strategies.
Camps, Excursions,
Sports Days, Swimming lessons:
Support is provided for these activities through a range of
measures ranging from liaison with parents or teachers to discuss the student
specific needs, putting in place some of these strategies and the distribution
of this information to other stakeholders. Support staff may review processes
and timelines with students for whom this is a need. Independence and Self
advocacy are supported through judicious use and appropriate fading of prompts.
Communication from our school
Parents are strongly encouraged to read the school newsletter which is published to
the website several times per term. There is extensive information available on
the school website as well. Some
important notices are listed on the electronic
board at the front of the school. It is also recommended that parents download and install the QSchools app on
tablet or smart phone. This app enables rapid access to newsletters and other
information on portable devices. It is also suggested that parents register for
QParents.
Contact with staff
Teachers (Class Teachers or Support Teachers) are the staff
members able to discuss a student's educational progress with a parent but of
course we seek and encourage a warm and friendly relationship between all
members of the students’ support teams. Parents are encouraged to make
appointments with staff rather than seeking extensive impromptu feedback to
ensure focus can be directed.
Curriculum
Schools have an obligation to ensure equity of access to the
Australian
Curriculum for all students. All students are entitled to participate
in the Australian Curriculum for their age cohort. Students with disability may have their
learning focus adjusted to meet their individual needs. This may include:
adjustments to the teaching and learning strategies offered to the class cohort, e.g. visual aids supporting students to follow a learning sequence or their timetable adjustments within the general capabilities targeting literacy, numeracy, and personal and social capability learning, e.g. focused literacy or social skills development through a science lesson.
Curriculum provision for some students with disability may also support the development of adaptive skills, e.g. communicating, safe behaviours, etc.
adjustments: measures–or actions–taken by an education provider that assist a student with disability to participate on the same basis as a student without disability
Explicit Instruction used by all teachers- research based pedagogy proven to particularly support students with disability forms the cornerstone of instruction at Bounty Boulevard and supports Differentiation.
Homework
Students are provided with homework in line the school’s
policy. If you feel the allocated work needs adjustment or presents other difficulties,
please speak with your child’s class teacher or Support Teacher to discuss
options.
Personalised Learning
Records
An overview of support and adjustments for the SEP students and
students with other disabilities is reviewed each year with input from Class
Teacher, Support Teacher and Parents. Depending upon student need, this can
take different forms.
Information to
Specialist Teachers: Information about students with advice as to support
strategies for individual students is provided to Specialist Staff including
PE, Music and other specialist teachers in a brief overview. They liaise with
class teacher for specifics. Class teacher may seek advice from support teacher.
Medical and Therapy
reports provided by parents/carers to the school:
The school values these documents. Reports provided to the
school are useful in planning adjustments for students.
Sometimes parents may have forms and/or reports they need
for Paediatric visits. Staff generally need two weeks’ notice to complete these
as there is often considerable collaboration with others required. If you know
even further ahead of these appointments and inform us, this ensures best data
collection.
Medication
Students who need medication administered at school go
through the First Aid room, where forms are signed by parents. Please let your
child’s class teacher know if there are changes or if there are issues around
this at school.
NAPLAN and other
Assessments:
Adjustments to Assessments are available to students considered
under disability legislation for NAPLAN testing. The types of adjustments allowed are regulated
by the testing authority and are designed to allow students to demonstrate
their knowledge. Some adjustments are available for other assessments.
Nationally Consistent
Collection of Data (NCCD):
A survey
of all students under the broad category of disability within schools is
completed each year by all schools in Australia. The information provided to
government will enable better targeting of support and resources to benefit
students with disability.
Parent Information:
To assist with planning it is important that parents inform
the Class Teacher of any upcoming changes which may affect your child. Emails
are often a good way to maintain contact.
If you feel there are issues you need to discuss with staff, it is
important to make an appointment so that time & focus can be allocated to
meetings.
Sensory and
Environmental Supports in Class:
Teachers support students by facilitating the use of sensory
and environmental supports such as Move n Sit cushion, pencil grips, Visual
Timetables, withdrawal chill out zones, take a break systems, focus mats and
ear muffs to name a few. Trial materials are often available through the
school. Use and implementation is considered through information including
Therapy reports. The program is co-ordinated through ‘Tools for Learning’ framework which teaches students and peers
about such supports and about equity vs equality.
Social Skills:
Students are supported through the PBL (Positive Behaviour
for Learning) program in classes. Regular Circle Time sessions occur in classes
which are a research based approach to building confidence and resolving
conflict. Other programs, are provided through various departments.
Support at Breaks:
Bounty Boulevard offers numerous lunch time supervised Play
options including: Chess Club, Supernova Play, Technology clubs, Cooking, art
and sport. Some students may be required or encouraged to attend at certain
times in order to support interactions. The goal of programs differs among
students. Rationale may include: social skilling in readiness for joining
playground, time to de-stress in structured environment in preparation for
improved focus in class, opportunity to invite a friend to play to build a
relationship which may translate to the playground and supervision of eating
for medical reasons.
Transitions
We have a differentiated program to transition students to
Prep. It encompasses a range of measures. The program includes a tour of the
school, a class visit by student, student activities with class and parent
information session, visit to their new Prep class and teacher in the week
prior to school beginning.
To support students to transition between year levels,
students visit classes in the area of the school where the next year level are
likely to be situated. They learn to find toilets, eating areas and other areas
they will use in their new class. They meet some staff from the new year level.
We work with feeder state high schools to support students in the transition
programs provided by those schools.
We look forward to a rewarding
partnership between Staff, Parents/Carers and our students as we seek to build
their resilience, confidence and skills to take their place in Queensland’s
economy and society.
Head of Diverse Learners.
Updated 11/02/2018 Information contained in this booklet came
from DET Learning Place and DET Policy documents.